CK Physiotherapy
AREAS COVERED
W7, W5, W13, Ealing, West London
57 Elthorne Avenue
Hanwell, W7 2JY
T: 020 8566 4113
M: 079 572 46185
E: info@ckphysio.co.uk
Location / Parking
We are situated in Hanwell, between Boston Manor Road and Northfields Avenue, south of the Uxbridge Road.57 Elthorne Avenue
Hanwell, W7 2JY
There are parking restrictions Mon - Fri 9-10am and 2-3pm. If you need a permit during this time please inform your therapist when you arrive. There are no parking restrictions at other times.
Opening Times
Please phone the number above during working hours to make an appointment. Our reception service will be happy to book your session.
London Underground / Bus Services
London Underground
10 min. walk from Boston Manor Tube Station.
15 min. walk from Northfields Tube Station.
Bus Service
E8, E3, E2, 207, 607, 83
Request Call Back
Our Blog
Key Benefits of Electrotherapy in Physiotherapy Treatments
By: BryanKelly (Psst, View author in Google Plus) Date: Sep 19th, 2019Physiotherapists use a variety of tools to manage pain, restore range of motion, and treat conditions of the musculoskeletal system. Along with methods like joint mobilisation, stretching, and targeted exercises, your physiotherapist might recommend electrotherapy as a treatment option.
Using specialised devices designed to deliver customised levels of electrical stimulation to your body's nerves, muscles, or tendons, trained physiotherapists can harness the power of electrotherapy to promote treat injuries, promote healing, and offer pain relief.
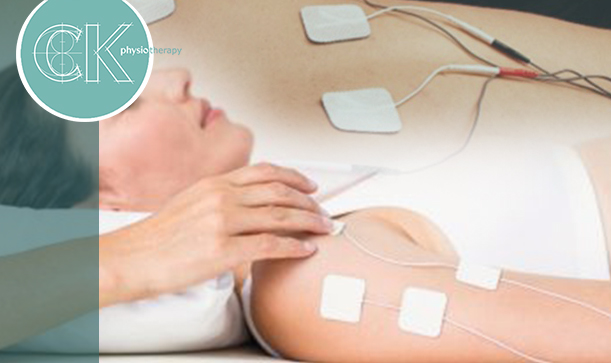
Electrotherapy: What it is & How it Works
A powerful tool used by many physiotherapists, electrotherapy treats chronic pain, musculoskeletal injuries, muscle wasting, and nerve pain by using targeted and controlled electrical stimulation.
Electrotherapy is a gentle and non-invasive modality that works by stimulating nerves and muscles through the surface of the skin. Though it varies based on which device your practitioner uses, electrotherapy is thought to work in a variety of ways:
• Send out electrical impulses that block or interfere with the body's pain signals, leading to reduced pain.
• Help release endorphins (chemical messengers) that naturally decrease pain in the body.
• Stimulate muscle tissue to contract to reduce atrophy.
• Create a heating effect within the body which improves circulation and stimulates healing.
• Stimulate cells which reduce inflammation, promote collagen production, and inhibit pain.
6 Main Types of Electrotherapy Treatment
Though there are many types of electrotherapy treatments available, most sessions involve the same basic set up. In some forms, you will have electrode pads placed on your skin with adhesives. The pads are connected to via wire to the physiotherapist's battery-powered device — which then transmits the electrical signals to your body.
In other forms of electrotherapy, your physiotherapist will use a transducer with gel to transmit specialised ultrasound waves into your body. When you go for a session, your physiotherapist might use one of these methods in treatment:
1. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
6. Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
One of the most common electrotherapy treatments, Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) makes use of small devices which deliver pulses of electrical stimulation. The goal of the TENS machine is to stimulate sensory nerves to achieve pain relief and is often used for both nerve pain and chronic pain conditions.
Therapeutic Ultrasound
When used in physiotherapy, therapeutic ultrasound in physiotherapy uses a deep heating effect on different tissues — like muscles, ligaments, and tendons — to boost circulation and stimulate the healing process. This method makes use of a transducer instead of electrode pads and is often used to treat strains, tendonitis, and knee meniscus tears.
Interferential
Also known as IFT, interferential electrotherapy uses low-frequency electrical stimulation to stimulate muscles, increase blood flow, and reduce pain. IFT is sometimes used for patients who dislike the sensation of TENS electrotherapy.
Electroacupuncture
Ordinarily, acupuncture makes use of thin needles inserted at specific points which target different organs or bodily systems. Electroacupuncture follows the same principles, except it uses two needles with an electric current that passes between them. It's often used to treat chemotherapy side effects and acute pain.
Shockwave Therapy
In shockwave therapy, acoustic waves with high energy are used to treat conditions. Like therapeutic ultrasound, shockwave therapy makes use of a transducer with gel. This therapy is used to help stimulate collagen production, release painful trigger points, and reduce inflammation in the body. It's also very useful for musculoskeletal conditions like plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, and Achilles tendinopathy.
Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)
While some methods of electrotherapy target nerves, EMS targets muscle tissue. This specialised form of electrotherapy stimulates your motor neurons which causes your muscles to contract. This is often used in cases to treat and prevent muscle atrophy.
6 Benefits of Electrotherapy in Physiotherapy Treatments
Your physiotherapist can help you figure out which electrotherapy method works best for you and your needs. Depending on your medical or musculoskeletal condition, electrotherapy can offer several key benefits:
2. Promote healing of musculoskeletal injuries.
3. Have a non-invasive, drug-free pain control.
5. Increase circulation for wound repair.
6. Have a minimal to no side effects.
1. Reduce nerve pain.
Those who suffer from nerve pain experience numbness, tingling, burning, muscle weakness, and general pain throughout the body. Though the causes for nerve pain vary, the pain is attributed to your body's nerves sending out electrical impulses that carry pain signals. In cases of nerve pain, a physiotherapist can use a TENS machine to target and reduce nerve pain by interfering with or "confusing" the pain signals your body transmits.
2. Promote healing of musculoskeletal injuries.
Some electrotherapy modalities, especially a shockwave therapy treatment, have been shown to effectively treat a variety of musculoskeletal conditions. Not only can shockwave therapy reduce pain, but it can help increase blood flow to an injured area which can stimulate the healing process. You might find that shockwave therapy is useful for injuries like:
• Tennis elbow
• Plantar fasciitis
• Carpal tunnel syndrome
• Jumpers knee
• Shoulder pain and injuries
Because electrotherapy can help increase circulation and promote healing in an area, it's also used by physiotherapists to treat common sports injuries like sprains and strains.
3. Have a non-invasive, drug-free pain control.
Electrotherapy offers a safe, non-toxic, and non-addictive way to handle chronic pain. Whether you suffer from chronic neck or back pain, you know that these conditions can make it difficult to perform activities of daily living and can reduce your quality of life.
Though pain-reducing medication is sometimes a necessary intervention, using electrotherapy for pain relief offers a powerful alternative — without any of the concerns inherent in using habit-forming drugs. In addition, electrotherapy offers a non-invasive way to handle chronic pain and promote tissue repair. Using electrotherapy can, in some cases, prevent the need for invasive interventions like surgery.
4. Prevent muscle atrophy.
When muscles can't be used due to injury, illness, or nerve damage, this can result in muscle atrophy — which is when a muscle wastes away. Not only does muscle atrophy restrict movement and impact quality of life, but it can also contribute to pain and stiffness. Fortunately, electrotherapy — specifically electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) — can help prevent atrophy by stimulating muscles to contract. Sometimes, EMS is used to stimulate muscles to contract, while a TENS machine is used to help reduce the pain associated with atrophy.
5. Increase circulation for wound repair.
Healthy circulation is an incredibly important aspect of the healing process. Oxygenated blood brings nutrients to our cells and helps jump-start tissue healing. In addition, healthy circulation helps remove toxins from the body to create a healthier body. Studies have shown that electrotherapy devices can significantly enhance blood flow in the body — which then boosts the body's ability to heal and repair wounds.
6. Have a minimal to no side effects.
When it comes to electrotherapy treatments, most patients experience pain relief and healing with relatively few side effects. In fact, the most common side effect from electrotherapy can often be traced back to the adhesives used in securing the electrode pad to the skin, which can occasionally trigger a rash or allergic reaction on the site. You may experience some slight discomfort during treatment, but electrotherapy is generally a pain-free methodology with no long-lasting side effects.
Visit a Trusted Physiotherapist in London
If you are currently experiencing chronic pain or are struggling with musculoskeletal conditions or injuries, then electrotherapy might be a good option for you. To ensure you receive professional care from educated professionals, seek a qualified physiotherapist in London who offers electrotherapy treatment.
Want to learn more? Reach out to the caring and compassionate team at CK Physio to get started.
Related info articles
What is Electrotherapy Treatment and How Does It Work